Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance and inadequate insulin production. If you looking for type 2 diabetes treatment then you take Metformin HCL 500 mg to treat type 2 diabetes. It is a serious health concern affecting millions of people worldwide, with the potential for severe complications if left untreated. Recognizing the early warning signs of type 2 diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis, management, and prevention of complications.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that affects how your body processes glucose, the primary source of energy for cells. Take Metformin Hydrochloride 500 mg to cure Type 2 Diabetes. Normally, insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells. In type 2 diabetes, cells become resistant to insulin, and the pancreas may not produce enough insulin to compensate, leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia).
Several factors contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes, including genetics, lifestyle choices, obesity, sedentary behavior, and age. While some risk factors like genetics cannot be modified, lifestyle modifications such as adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes or delay its onset.
Early Warning Signs of Type 2 Diabetes
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria): One of the earliest and most common signs of type 2 diabetes is increased urination. Excess glucose in the bloodstream can lead to increased urine production as the kidneys work to eliminate the excess sugar. Individuals may find themselves urinating more frequently, especially at night (nocturia), disrupting sleep patterns.
- Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia): Along with frequent urination, excessive thirst is another hallmark symptom of type 2 diabetes. The body tries to compensate for fluid loss through urination by triggering thirst signals, leading to increased water intake. Despite drinking more fluids, individuals may still feel persistently thirsty.
- Increased Hunger (Polyphagia): Despite eating regular meals, individuals with undiagnosed type 2 diabetes may experience heightened hunger or unexplained weight loss. The inability of cells to effectively utilize glucose for energy can result in increased appetite and a feeling of constant hunger, even after consuming adequate calories.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Type 2 diabetes can cause feelings of fatigue, weakness, and overall low energy levels. The cells’ inability to access glucose for energy production can lead to a general sense of tiredness, even after getting sufficient rest.
- Blurry Vision: Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can affect the lens of the eye, leading to blurred vision or difficulty focusing. Individuals with undiagnosed or poorly controlled type 2 diabetes may notice changes in their vision, such as blurred or distorted images.
- Slow Healing of Wounds: High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds and injuries. Minor cuts, bruises, or infections may take longer to heal, increasing the risk of complications.
- Frequent Infections: Type 2 diabetes can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. Recurring infections, particularly urinary tract infections (UTIs), skin infections, or fungal infections like thrush, may be early indicators of diabetes.
- Tingling or Numbness: Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. Symptoms may include tingling, numbness, or a burning sensation, typically starting in the hands and feet.
- Darkened Skin Patches (Acanthosis Nigricans): In some cases, darkened, velvety patches of skin, known as acanthosis nigricans, may develop in areas such as the neck, armpits, or groin. This skin condition is associated with insulin resistance and may be a visible sign of underlying metabolic changes.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) and High Cholesterol: Individuals with type 2 diabetes are at an increased risk of developing other metabolic conditions such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels. These conditions often coexist and contribute to cardiovascular complications if not managed effectively.
Seeking Medical Evaluation
If you experience any of these warning signs or suspect you may have type 2 diabetes, it is essential to seek medical evaluation promptly. A healthcare professional can perform blood tests, such as fasting blood glucose tests or hemoglobin A1c tests, to diagnose diabetes and assess your overall health.
Early diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and lifestyle interventions to manage blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Treatment strategies may include dietary changes, regular physical activity, medication (such as oral antidiabetic drugs or insulin), monitoring of blood glucose levels, and ongoing medical follow-ups.
Prevention and Management
While type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition, proactive measures can help prevent its onset or delay its progression:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity and excess body weight are significant risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
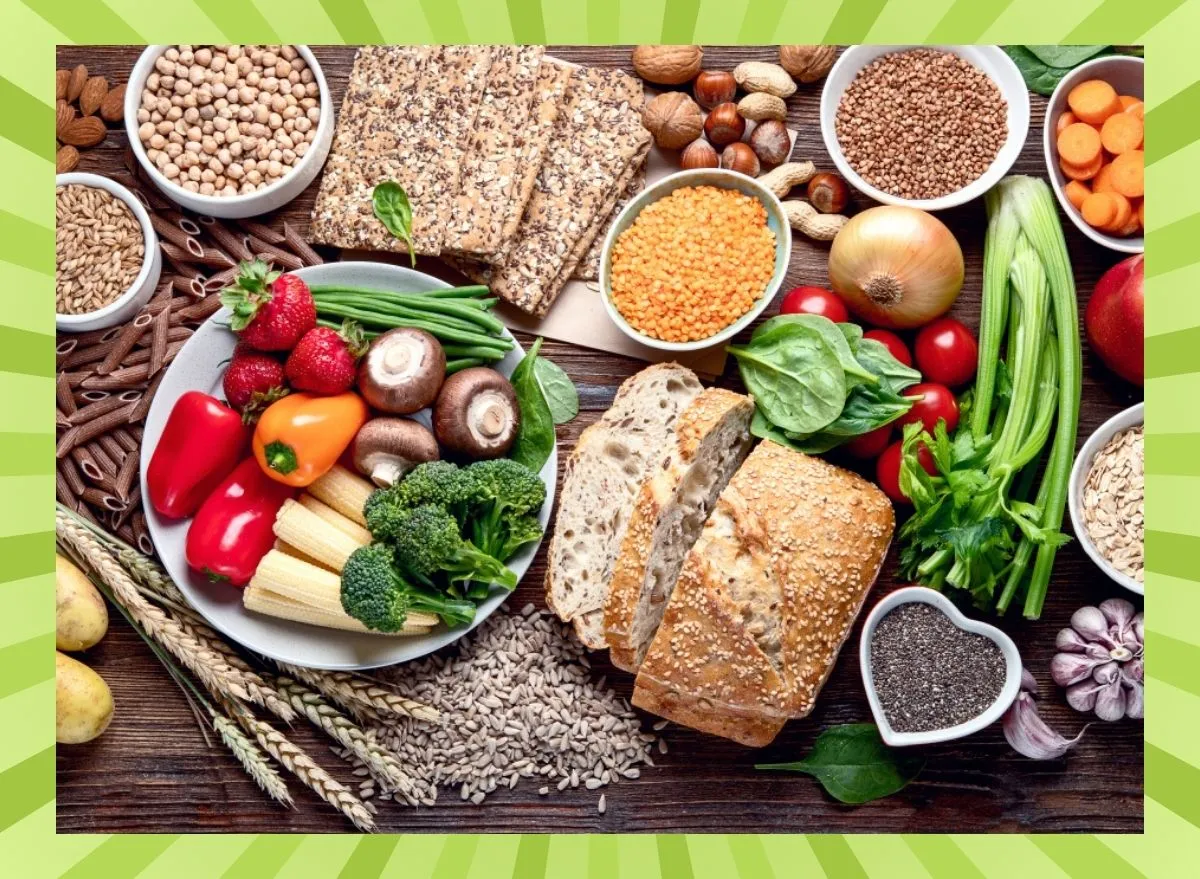
- Follow a Balanced Diet: Adopting a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting sugar, refined carbohydrates, and processed foods can help regulate blood sugar levels and support overall health.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Regular exercise is essential for improving insulin sensitivity, managing weight, and promoting cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
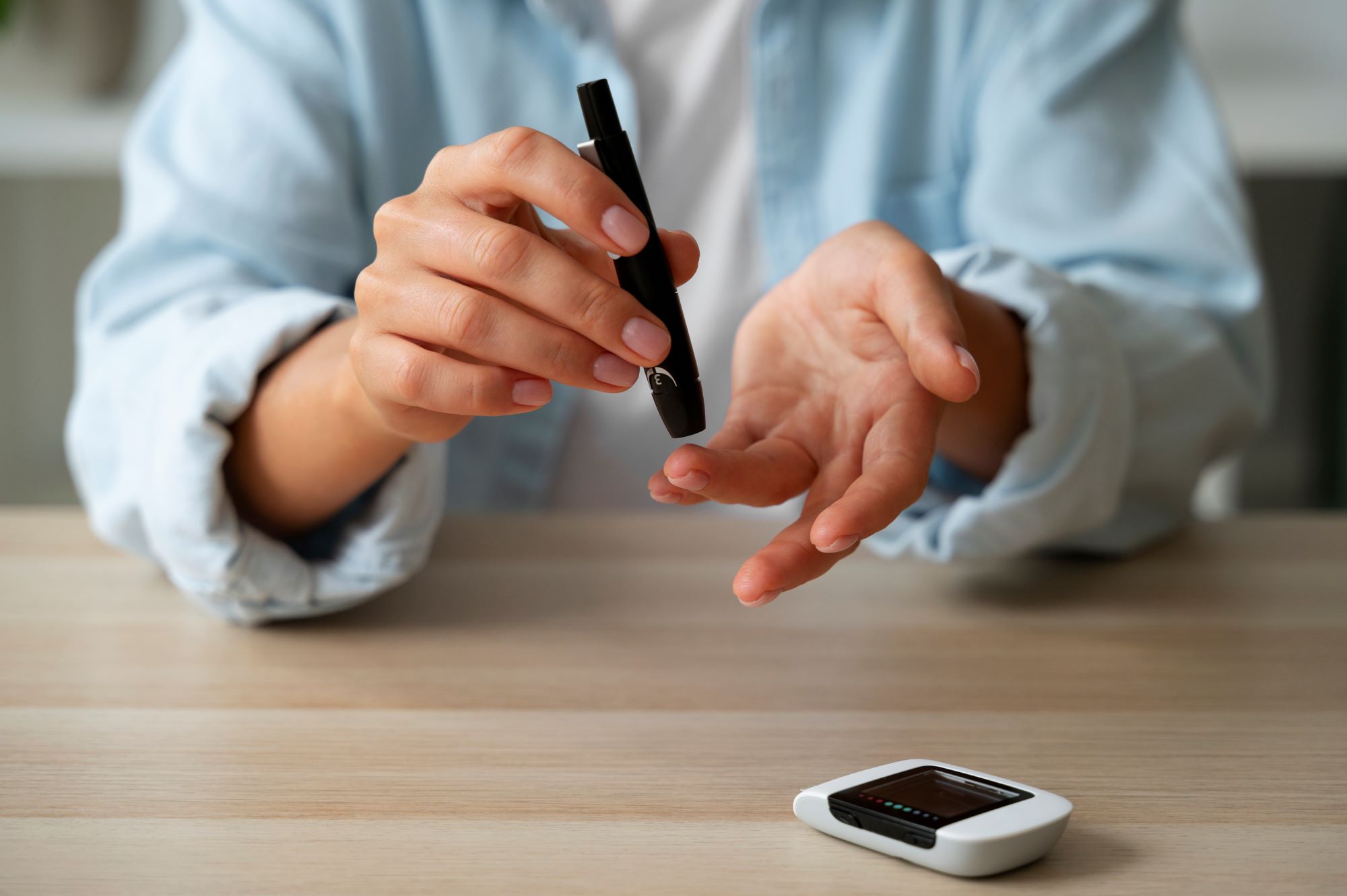
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: If you have prediabetes or are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly can help track changes and guide preventive measures or treatment interventions.
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen insulin resistance and increase the risk of diabetes complications. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can have significant benefits for overall health.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress and poor stress management can contribute to insulin resistance and affect blood sugar control. Practice relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and stress-reducing activities to improve overall well-being.
- Get Regular Health Check-ups: Routine health screenings, including blood pressure checks, cholesterol tests, and diabetes screenings, are essential for early detection and management of metabolic conditions.
In conclusion, recognizing the early warning signs of type 2 diabetes is crucial for timely diagnosis, intervention, and management. By staying informed, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and seeking medical guidance when needed, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or effectively manage type 2 diabetes and improve long-term health outcomes.